5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Cancer Archive
Articles
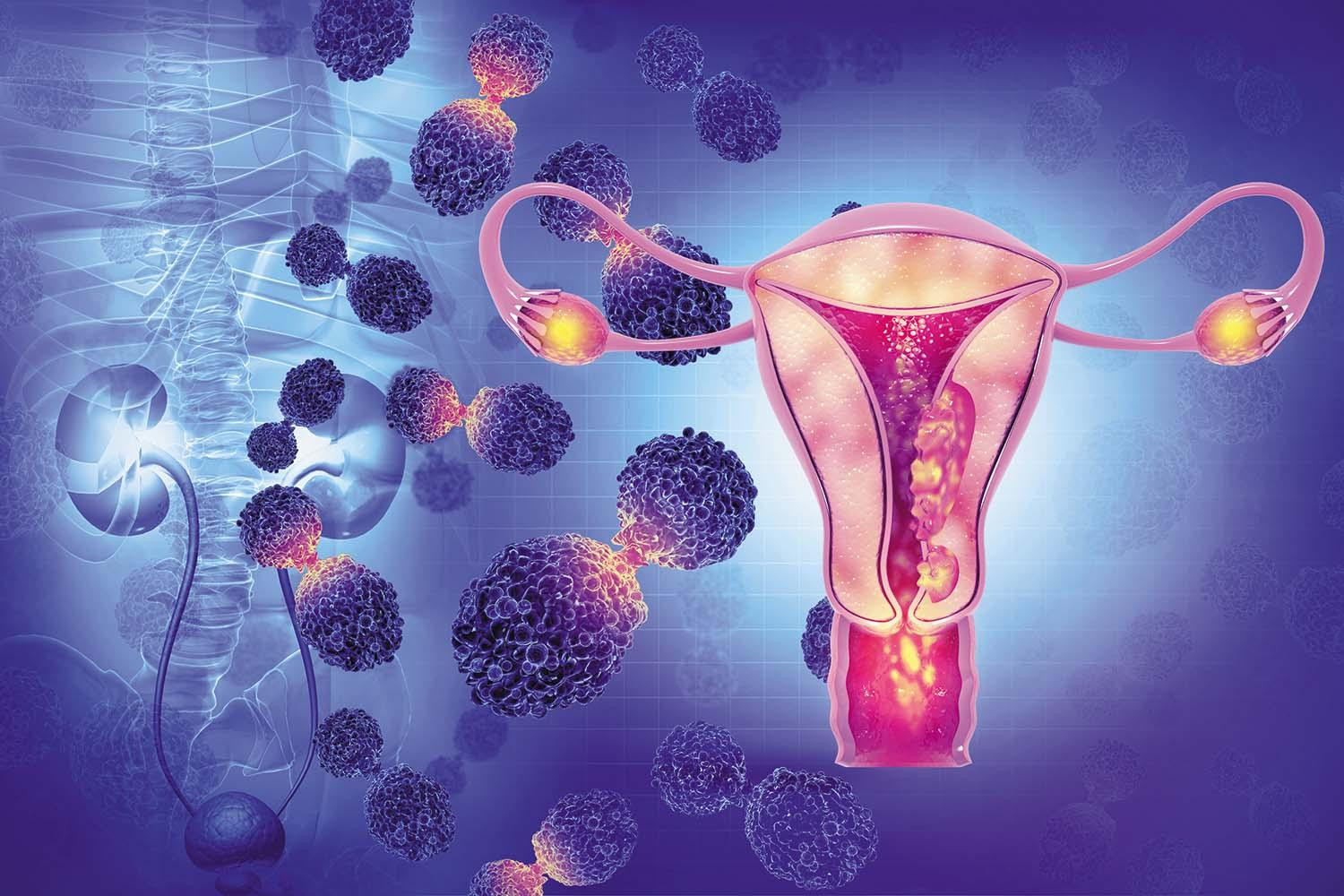
What raises your risk for gynecologic cancer?
Gynecologic cancers, which affect the ovaries, uterus, cervix, vagina, or vulva, are less common than breast cancer. Women can guard against these cancers by learning the risk factors for each type, which include obesity, exposure to human papillomavirus, and smoking. Women should also continue pelvic exams and cervical cancer screenings after a hysterectomy or menopause, as well as watch for unusual symptoms. Women with a strong family history of gynecologic or certain other cancers should consider genetic testing.
DASH diet tied to lower colorectal cancer risk
A 2025 research review found that adhering to the DASH diet—which emphasizes eating fruits, vegetables, lean protein, whole grains, nuts, and low-fat dairy products—is linked to a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Exercise boosts colon cancer survival
In a 2025 study of about 900 people treated for colon cancer (followed for an average of eight years), people who took part in a supervised exercise program for three years had about 30% better odds of surviving, compared with people who weren’t in the program.
Physical activity of any intensity tied to lower cancer risk
In a 2025 study of more than 85,000 people (average age 63), followed for six years, those who were the most active—even if they were simply doing light-intensity activities—had a 26% lower risk for cancer, compared with those who were least active.
Calcium may cut odds of colorectal cancer, while alcohol may boost them
A 2025 study suggested that boosting dietary calcium intake may reduce the odds of developing colorectal cancer, while drinking more alcohol may raise risks for the disease.
The cancer–heart disease connection
Cancer survivors are more likely to die of heart disease than from cancer-related complications. One reason is that certain cancer treatments can cause cardiovascular complications. But the two diseases share many root causes, including tobacco use and obesity, as well as diabetes and high cholesterol. Growing evidence suggests that people with heart disease may be more likely to develop cancer.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up