5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Heart Disease Archive
Articles
The latest on lipoprotein(a), an inherited cause of early heart disease
About 20% of people have high blood levels of lipoprotein(a)—Lp(a) for short—a fatty particle that's like the evil twin of the more familiar LDL ("bad") cholesterol. Elevated Lp(a) which can double or triple risk of a heart attack and raise stroke risk, and is linked to problems with the heart's aortic valve. With new treatments that can lower Lp(a) on the horizon, cardiologists are now testing more people for this biomarker, which is not included in standard cholesterol tests.
When cancer treatment affects the heart
Side effects from both older and newer cancer therapies can affect the heart and blood vessels, possibly causing serious, sometimes life-threatening complications. People diagnosed with any type of cancer should ask their doctor whether their planned treatment might lead to cardiovascular problems. Those ages 65 and older and anyone with risk factors for heart disease (such as high blood pressure or diabetes) may want to request a referral to a cardio-oncologist. These specialists focus on preventing and managing cardiovascular problems in people who are undergoing (or have completed) treatment for cancer.
What is vasculitis?
Vasculitis is characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, including the arteries, veins, and capillaries. The resulting damage can narrow, weaken, or scar vessels that supply just one body part or many different organs.
Protect yourself from cardiovascular disease
A 2022 report predicts higher rates of cardiovascular disease (CVD)—heart disease, heart attack, heart failure, and stroke—over the next three decades. Older adults can lower their CVD risk by managing high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and excess weight. Also, they should follow the big three healthy-heart habits: a plant-based diet, sufficient amount of recommended exercise, and at least seven hours of sleep.
Illicit drugs linked to higher risk of atrial fibrillation
Using recreational drugs—including methamphetamine, opiates, cocaine, or cannabis—may increase a person's risk for atrial fibrillation.
Sleep apnea treatment lowers rehospitalization for heart problems in older adults
A 2022 study found that older adults with sleep apnea who are hospitalized for cardiovascular disease are far less likely to be rehospitalized within 30 days if they consistently treat their apnea with CPAP therapy, which keeps the airway open during sleep.
Drinking coffee linked to healthier hearts and longer lives
A 2022 study found that coffee drinkers were less likely to develop irregular heartbeats, cardiovascular disease, heart-related deaths, and deaths from any cause over a 12-year period, compared with people who did not drink coffee.
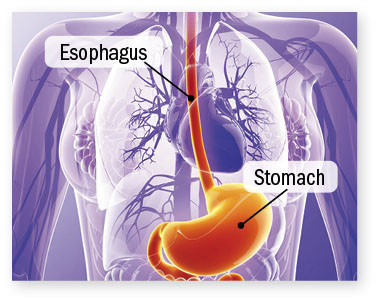
Heart disease and heartburn: What's the overlap?
Heartburn can cause chest pain that may be mistaken for a heart attack, and vice versa. Heartburn causes more a burning sensation and is more likely to occur after a large meal. Heart attacks are often described as a feeling of tightness or pressure and are more likely to occur after physical activity or stress. People who aren't sure about their symptoms should get to an emergency room for an evaluation as soon as possible.
Shining a light on thoracic aortic disease
A thoracic aortic aneurysm can be small and stable, or it can tear or rupture. People with certain genetic conditions, and those who have a relative who has had this condition, are at higher risk and should be tested.
Poor physical function may predict cardiovascular disease
A new study suggests that older adults who maintain an high level functional fitness have a lower their risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke compared with those who are not as fit.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up